Win32 Windows Volume Program and Code Example 20
Master File Table Program Example 1
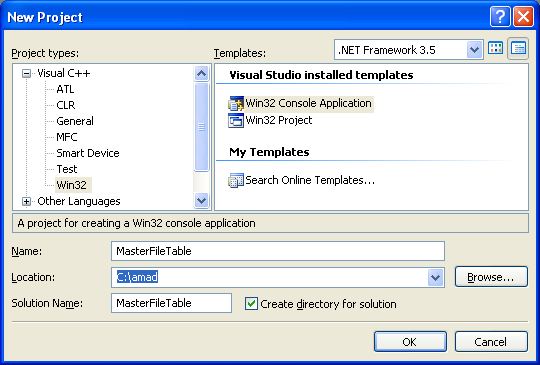
The following program example tries to read the Master File Table and extract some of the information. Create a new Win32 console application project and give a suitable project name.
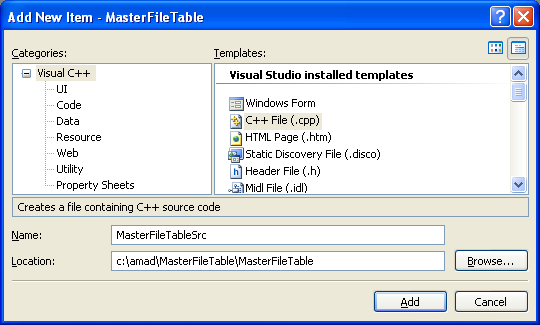
Add the source file and give a suitable name.
Add the following source code.
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <winioctl.h>
// Format the Win32 system error code to string
void ErrorMessage(DWORD dwCode);
int wmain(int argc, WCHAR **argv)
{
HANDLE hVolume;
LPWSTR lpDrive = L\\\\.\\c:;
// {0} ~ ZeroMemory()
PNTFS_VOLUME_DATA_BUFFER ntfsVolData = {0};
// NTFS_EXTENDED_VOLUME_DATA versionMajMin = {0};
BOOL bDioControl = FALSE;
DWORD dwWritten = 0;
hVolume = CreateFile(lpDrive,
GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_WRITE,
FILE_SHARE_READ | FILE_SHARE_WRITE,
NULL,
OPEN_EXISTING,
0,
NULL);
if(hVolume == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
wprintf(LCreateFile() failed!\n);
ErrorMessage(GetLastError());
if(CloseHandle(hVolume) != 0)
wprintf(LhVolume handle was closed successfully!\n);
else
{
wprintf(LFailed to close hVolume handle!\n);
ErrorMessage(GetLastError());
}
exit(1);
}
else
wprintf(LCreateFile() is pretty fine!\n);
ntfsVolData = (PNTFS_VOLUME_DATA_BUFFER)malloc(sizeof(NTFS_VOLUME_DATA_BUFFER)+sizeof(NTFS_EXTENDED_VOLUME_DATA));
if(ntfsVolData == NULL)
wprintf(LInsufficient memory!\n);
else
wprintf(LMemory allocated successfully!\n);
// a call to FSCTL_GET_NTFS_VOLUME_DATA returns the structure NTFS_VOLUME_DATA_BUFFER
bDioControl = DeviceIoControl(hVolume, FSCTL_GET_NTFS_VOLUME_DATA, NULL, 0, ntfsVolData,
sizeof(NTFS_VOLUME_DATA_BUFFER)+sizeof(NTFS_EXTENDED_VOLUME_DATA), &dwWritten, NULL);
// Failed or pending
if(bDioControl == 0)
{
wprintf(LDeviceIoControl() failed!\n);
ErrorMessage(GetLastError());
if(CloseHandle(hVolume) != 0)
wprintf(LhVolume handle was closed successfully!\n);
else
{
wprintf(LFailed to close hVolume handle!\n);
ErrorMessage(GetLastError());
}
exit(1);
}
else
wprintf(LDeviceIoControl() is working...\n\n);
wprintf(LVolume Serial Number: 0X%.8X%.8X\n,ntfsVolData->VolumeSerialNumber.HighPart, ntfsVolData->VolumeSerialNumber.LowPart);
wprintf(LThe number of bytes in a cluster: %u\n,ntfsVolData->BytesPerCluster);
wprintf(LThe number of bytes in a file record segment: %u\n,ntfsVolData->BytesPerFileRecordSegment);
wprintf(LThe number of bytes in a sector: %u\n,ntfsVolData->BytesPerSector);
wprintf(LThe number of clusters in a file record segment: %u\n,ntfsVolData->ClustersPerFileRecordSegment);
wprintf(LThe number of free clusters in the specified volume: %u\n,ntfsVolData->FreeClusters);
wprintf(LThe starting logical cluster number of the master file table: 0X%.8X%.8X\n,ntfsVolData->MftStartLcn.HighPart,ntfsVolData->MftStartLcn.LowPart);
wprintf(LThe starting logical cluster number of the master file table mirror: 0X%.8X%.8X\n,ntfsVolData->Mft2StartLcn.HighPart, ntfsVolData->Mft2StartLcn.LowPart);
wprintf(LThe length of the master file table, in bytes: %u\n,ntfsVolData->MftValidDataLength);
wprintf(LThe starting logical cluster number of the master file table zone: 0X%.8X%.8X\n,ntfsVolData->MftZoneStart.HighPart,ntfsVolData->MftZoneStart.LowPart);
wprintf(LThe ending logical cluster number of the master file table zone: 0X%.8X%.8X\n,ntfsVolData->MftZoneEnd.HighPart, ntfsVolData->MftZoneEnd.LowPart);
wprintf(LThe number of sectors: %u\n,ntfsVolData->NumberSectors);
wprintf(LTotal Clusters (used and free): %u\n,ntfsVolData->TotalClusters);
wprintf(LThe number of reserved clusters: %u\n,ntfsVolData->TotalReserved);
// To extract this info the buffer must be large enough, however...FAILED!
//wprintf(LByte returns: %u\n, versionMajMin.ByteCount);
//wprintf(LMajor version: %u\n, versionMajMin.MajorVersion);
//wprintf(LMinor version: %u\n, versionMajMin.MinorVersion);
if(CloseHandle(hVolume) != 0)
wprintf(L\nhVolume handle was closed successfully!\n);
else
{
wprintf(L\nFailed to close hVolume handle!\n);
ErrorMessage(GetLastError());
}
// free up the allocated memory by malloc()
free(ntfsVolData);
return 0;
}
// Accessory function converting the GetLastError() code
// to a meaningful string
void ErrorMessage(DWORD dwCode)
{
// get the error code...
DWORD dwErrCode = dwCode;
DWORD dwNumChar;
LPWSTR szErrString = NULL; // will be allocated and filled by FormatMessage
dwNumChar = FormatMessage( FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER |
FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM, // use windows internal message table
0, // 0 since source is internal message table
dwErrCode, // this is the error code number
0, // auto-determine language to use
(LPWSTR)&szErrString, // the message
0, // min size for buffer
0 ); // since getting message from system tables
if(dwNumChar == 0)
wprintf(LFormatMessage() failed, error %u\n, GetLastError());
//else
// wprintf(LFormatMessage() should be fine!\n);
wprintf(LError code %u:\n %s\n, dwErrCode, szErrString) ;
// This buffer used by FormatMessage()
if(LocalFree(szErrString) != NULL)
wprintf(LFailed to free up the buffer, error %u\n, GetLastError());
//else
// wprintf(LBuffer has been freed\n);
}
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is an output sample.

You can compare the result with the fsutil, the Windows file system utility.
