The Windows Processes and Threads 25
Using Fibers Program Example
The CreateFiber() function creates a new fiber for a thread. The creating thread must specify the starting address of the code that the new fiber is to execute. Typically, the starting address is the name of a user-supplied function. Multiple fibers can execute the same function. The following example demonstrates how to create, schedule, and delete fibers. The fibers execute the locally defined functions ReadFiberFunc() and WriteFiberFunc(). This example implements a fiber-based file copy operation. When running the example, you must specify the source and destination files. Note that there are many other ways to copy file programmatically; this example exists primarily to illustrate the use of the fiber functions.
Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.
Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.
Next, add the following source code.
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void __stdcall ReadFiberFunc(LPVOID lpParameter);
void __stdcall WriteFiberFunc(LPVOID lpParameter);
void DisplayFiberInfo(void);
typedef struct
{
DWORD dwParameter; // DWORD parameter to fiber (unused)
DWORD dwFiberResultCode; // GetLastError() result code
HANDLE hFile; // handle to operate on
DWORD dwBytesProcessed; // number of bytes processed
} FIBERDATASTRUCT, *PFIBERDATASTRUCT, *LPFIBERDATASTRUCT;
#define RTN_OK 0
#define RTN_USAGE 1
#define RTN_ERROR 13
#define BUFFER_SIZE 32768 // read/write buffer size
#define FIBER_COUNT 3 // max fibers (including primary)
#define PRIMARY_FIBER 0 // array index to primary fiber
#define READ_FIBER 1 // array index to read fiber
#define WRITE_FIBER 2 // array index to write fiber
LPVOID g_lpFiber[FIBER_COUNT];
LPBYTE g_lpBuffer;
DWORD g_dwBytesRead;
int wmain(int argc, WCHAR *argv[])
{
LPFIBERDATASTRUCT fs;
// Validate arguments
if (argc != 3)
{
wprintf(LUsage: %s <SourceFile> <DestinationFile>\n, argv[0]);
wprintf(LExample: %s testsrcfile.txt testdstfile.txt\n,argv[0]);
// Returns 1
return RTN_USAGE;
}
// Allocate storage for the fiber data structures
fs = (LPFIBERDATASTRUCT)HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), 0, sizeof(FIBERDATASTRUCT) * FIBER_COUNT);
if (fs == NULL)
{
wprintf(LHeapAlloc() error %d\n, GetLastError());
return RTN_ERROR;
}
else
wprintf(LHeap was allocated for LPFIBERDATASTRUCT struct successfully!\n);
// Allocate storage for the read/write buffer
g_lpBuffer = (LPBYTE)HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
if (g_lpBuffer == NULL)
{
wprintf(LHeapAlloc() error %d\n, GetLastError());
return RTN_ERROR;
}
else
wprintf(LHeap was allocated for buffer successfully!\n);
// Open the source file
fs[READ_FIBER].hFile = CreateFile(
argv[1],
GENERIC_READ,
FILE_SHARE_READ,
NULL,
OPEN_EXISTING,
FILE_FLAG_SEQUENTIAL_SCAN,
NULL
);
if (fs[READ_FIBER].hFile == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
wprintf(LCreateFile() error %d\n, GetLastError());
return RTN_ERROR;
}
else
wprintf(LCreateFile() - file was opened for reading successfully!\n);
// Open the destination file
fs[WRITE_FIBER].hFile = CreateFile(
argv[2],
GENERIC_WRITE,
0,
NULL,
CREATE_NEW,
FILE_FLAG_SEQUENTIAL_SCAN,
NULL
);
if (fs[WRITE_FIBER].hFile == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
wprintf(LCreateFile() error %d\n, GetLastError());
return RTN_ERROR;
}
else
wprintf(LCreateFile() - file was created/opened for writing successfully!\n);
// Convert thread to a fiber, to allow scheduling other fibers
g_lpFiber[PRIMARY_FIBER]=ConvertThreadToFiber(&fs[PRIMARY_FIBER]);
if (g_lpFiber[PRIMARY_FIBER] == NULL)
{
wprintf(LConvertThreadToFiber() error %d\n, GetLastError());
return RTN_ERROR;
}
else
wprintf(LConvertThreadToFiber() is pretty fine!\n);
// Initialize the primary fiber data structure. We don't use
// the primary fiber data structure for anything in this sample.
fs[PRIMARY_FIBER].dwParameter = 0;
fs[PRIMARY_FIBER].dwFiberResultCode = 0;
fs[PRIMARY_FIBER].hFile = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
// Create the Read fiber
g_lpFiber[READ_FIBER]=CreateFiber(0,ReadFiberFunc,&fs[READ_FIBER]);
if (g_lpFiber[READ_FIBER] == NULL)
{
wprintf(LCreateFiber() error %d\n, GetLastError());
return RTN_ERROR;
}
else
wprintf(LCreateFiber() - read fiber was created successfully!\n);
fs[READ_FIBER].dwParameter = 0x12345678;
// Create the Write fiber
g_lpFiber[WRITE_FIBER]=CreateFiber(0,WriteFiberFunc,&fs[WRITE_FIBER]);
if (g_lpFiber[WRITE_FIBER] == NULL)
{
wprintf(LCreateFiber() error %d\n, GetLastError());
return RTN_ERROR;
}
else
wprintf(LCreateFiber() - write fiber was created successfully!\n);
fs[WRITE_FIBER].dwParameter = 0x54545454;
// Switch to the read fiber or schedules a fiber
// This function does not return a value.
SwitchToFiber(g_lpFiber[READ_FIBER]);
// We have been scheduled again. Display results from the
// read/write fibers
wprintf(LReadFiber: result code is %lu, %lu bytes processed\n,
fs[READ_FIBER].dwFiberResultCode, fs[READ_FIBER].dwBytesProcessed);
wprintf(LWriteFiber: result code is %lu, %lu bytes processed\n,
fs[WRITE_FIBER].dwFiberResultCode, fs[WRITE_FIBER].dwBytesProcessed);
// Delete the fibers
// This function does not return a value.
DeleteFiber(g_lpFiber[READ_FIBER]);
DeleteFiber(g_lpFiber[WRITE_FIBER]);
// Close handles
if(CloseHandle(fs[READ_FIBER].hFile) != 0)
wprintf(Lfs[READ_FIBER].hFile handle was closed successfully!\n);
else
wprintf(LFailed to close fs[READ_FIBER].hFile handle, error %d\n, GetLastError());
if(CloseHandle(fs[WRITE_FIBER].hFile) != 0)
wprintf(Lfs[WRITE_FIBER].hFile handle was closed successfully!\n);
else
wprintf(LFailed to close fs[WRITE_FIBER].hFile handle, error %d\n, GetLastError());
// Free allocated memory
if(HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, g_lpBuffer) != 0)
wprintf(LHeap for g_lpBuffer was freed!\n);
else
wprintf(LFailed to free g_lpBuffer heap, error %d\n, GetLastError());
if(HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, fs) != 0)
wprintf(LHeap for fs was freed!\n);
else
wprintf(LFailed to free fs heap, error %d\n, GetLastError());
return RTN_OK;
}
void __stdcall ReadFiberFunc(LPVOID lpParameter)
{
LPFIBERDATASTRUCT fds = (LPFIBERDATASTRUCT)lpParameter;
// If this fiber was passed NULL for fiber data, just return, causing the current thread to exit
if (fds == NULL)
{
wprintf(LPassed NULL fiber data, exiting current thread.\n);
return;
}
// Display some information pertaining to the current fiber
DisplayFiberInfo();
fds->dwBytesProcessed = 0;
while (1)
{
// Read data from file specified in the READ_FIBER structure
if (!ReadFile(fds->hFile, g_lpBuffer, BUFFER_SIZE, &g_dwBytesRead, NULL))
{
break;
}
// if we reached EOF, break
if (g_dwBytesRead == 0)
break;
// Update number of bytes processed in the fiber data structure
fds->dwBytesProcessed += g_dwBytesRead;
// Switch to the write fiber
// This function does not return a value.
wprintf(LSwitching to write fiber!\n);
SwitchToFiber(g_lpFiber[WRITE_FIBER]);
} // while
// Update the fiber result code
fds->dwFiberResultCode = GetLastError();
// Switch back to the primary fiber
wprintf(LSwitching to primary fiber!\n);
SwitchToFiber(g_lpFiber[PRIMARY_FIBER]);
}
void __stdcall WriteFiberFunc(LPVOID lpParameter)
{
LPFIBERDATASTRUCT fds = (LPFIBERDATASTRUCT)lpParameter;
DWORD dwBytesWritten;
// If this fiber was passed NULL for fiber data, just return,
// causing the current thread to exit
if (fds == NULL)
{
wprintf(LPassed NULL fiber data; exiting current thread.\n);
return;
}
else
wprintf(LSome fiber data was passed...\n);
// Display some information pertaining to the current fiber
DisplayFiberInfo();
// Assume all writes succeeded. If a write fails, the fiber
// result code will be updated to reflect the reason for failure
fds->dwBytesProcessed = 0;
fds->dwFiberResultCode = ERROR_SUCCESS;
while (1)
{
// Write data to the file specified in the WRITE_FIBER structure
if (!WriteFile(fds->hFile, g_lpBuffer, g_dwBytesRead,
&dwBytesWritten, NULL))
{
// If an error occurred writing, break
break;
}
// Update number of bytes processed in the fiber data structure
fds->dwBytesProcessed += dwBytesWritten;
// Switch back to the read fiber
wprintf(LSwitching to read fiber...\n);
SwitchToFiber(g_lpFiber[READ_FIBER]);
} // while
// If an error occurred, update the fiber result code...
fds->dwFiberResultCode = GetLastError();
// ...and switch to the primary fiber
wprintf(LSwitching to primary fiber...\n);
SwitchToFiber(g_lpFiber[PRIMARY_FIBER]);
}
void DisplayFiberInfo(void)
{
LPFIBERDATASTRUCT fds = (LPFIBERDATASTRUCT)GetFiberData();
LPVOID lpCurrentFiber = GetCurrentFiber();
// Determine which fiber is executing, based on the fiber address
if (lpCurrentFiber == g_lpFiber[READ_FIBER])
wprintf(LRead fiber entered...);
else
{
if (lpCurrentFiber == g_lpFiber[WRITE_FIBER])
wprintf(LWrite fiber entered...);
else
{
if (lpCurrentFiber == g_lpFiber[PRIMARY_FIBER])
wprintf(LPrimary fiber entered...);
else
wprintf(LUnknown fiber entered...);
}
}
// Display dwParameter from the current fiber data structure
wprintf(L(dwParameter is 0x%lx)\n, fds->dwParameter);
}
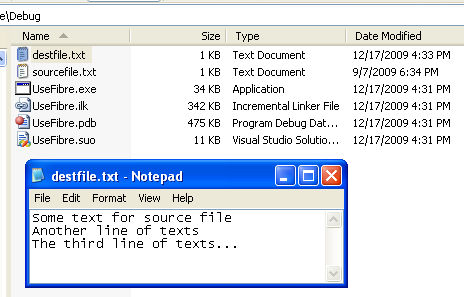
Build the project. Create a source file (in this case sourcefile.txt) under the project’s Debug folder and put some texts.
Run the project.
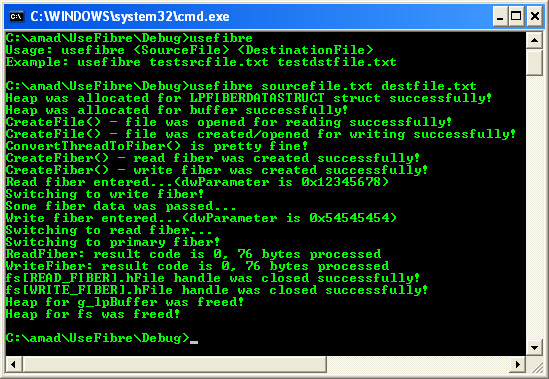
Check the destination file under the project’s Debug folder.
This example makes use of a fiber data structure which is used to determine the behavior and state of the fiber. One data structure exists for each fiber; the pointer to the data structure is passed to the fiber at fiber creation time using the parameter of the FiberProc() function. The calling thread calls the ConvertThreadToFiber() function, which enables fibers to be scheduled by the caller. This also allows the fiber to be scheduled by another fiber. Next, the thread creates two additional fibers, one that performs read operations against a specified file, and another that performs the write operations against a specified file. The primary fiber calls the SwitchToFiber() function to schedule the read fiber. After a successful read, the read fiber schedules the write fiber. After a successful write in the write fiber, the write fiber schedules the read fiber. When the read/write cycle has completed, the primary fiber is scheduled, which results in the display of the read/write status. If an error occurs during the read or write operations, the primary fiber is scheduled and example displays the status of the operation. Prior to process termination, the process frees the fibers using the DeleteFiber() function, closes the file handles, and frees the allocated memory.