Windows Services Programming 24
Another Program Example on How to Stop Windows Service
The following program example demonstrates how to programmatically stop a service by first stopping its dependencies. Create a new empty Win32 console application project for new solution. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.

Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.
Next, add the following source code.
//**********************************************************************
// This program demonstrates how to programmatically stop a service
// by first stopping its dependencies.
//
// THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED AS IS WITHOUT WARRANTY OF
// ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
// TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A
// PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
//
// Copyright (C) 1999 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
//**********************************************************************
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
//**********************************************************************
// StopService()
// PURPOSE : This function attempts to stop a service. It allows
// the caller to specify whether dependent services
// should also be stopped. It also allows a timeout
// value to be passed, to prevent a scenario in which a
// service shutdown hangs, and in turn the application stopping the service hangs.
// PARAMETERS: hSCM - open handle to the service control manager
// hService - open handle to the service to be stopped
// fStopDependencies - flag indicating whether to stop dependent services
// dwTimeout - maximum time (in milliseconds) to wait for the service and its dependencies to stop
// RETURN VALUE: If the operation is successful, ERROR_SUCCESS is
// returned. Otherwise, a Win32 error code is returned.
//**********************************************************************
DWORD StopService(SC_HANDLE hSCM, SC_HANDLE hService, BOOL fStopDependencies, DWORD dwTimeout)
{
SERVICE_STATUS ss;
DWORD dwStartTime = GetTickCount();
// Make sure the service is not already stopped
if (!QueryServiceStatus( hService, &ss) )
return GetLastError();
if (ss.dwCurrentState == SERVICE_STOPPED)
return ERROR_SUCCESS;
// If a stop is pending, just wait for it
while (ss.dwCurrentState == SERVICE_STOP_PENDING)
{
Sleep(ss.dwWaitHint);
if (!QueryServiceStatus(hService, &ss) )
return GetLastError();
if (ss.dwCurrentState == SERVICE_STOPPED)
return ERROR_SUCCESS;
if (GetTickCount() - dwStartTime > dwTimeout)
return ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
// If the service is running, dependencies must be stopped first
if (fStopDependencies)
{
DWORD i;
DWORD dwBytesNeeded;
DWORD dwCount;
LPENUM_SERVICE_STATUS lpDependencies = NULL;
ENUM_SERVICE_STATUS ess;
SC_HANDLE hDepService;
// Pass a zero-length buffer to get the required buffer size
if (EnumDependentServices( hService, SERVICE_ACTIVE, lpDependencies, 0, &dwBytesNeeded, &dwCount) )
{
// If the Enum call succeeds, then there are no dependent services so do nothing
wprintf(LThere are no dependencies for this service...\n);
}
else
{
if (GetLastError() != ERROR_MORE_DATA)
return GetLastError(); // Unexpected error
// Allocate a buffer for the dependencies
lpDependencies = (LPENUM_SERVICE_STATUS) HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY, dwBytesNeeded);
if ( !lpDependencies )
{
wprintf(LBuffer allocation for dependencies failed!\n);
return GetLastError();
}
__try {
// Enumerate the dependencies
if ( !EnumDependentServices(hService, SERVICE_ACTIVE, lpDependencies, dwBytesNeeded, &dwBytesNeeded, &dwCount) )
return GetLastError();
else
wprintf(LEnumDependentServices() is OK! Stopping the dependencies...\n);
for ( i = 0; i < dwCount; i++ )
{
wprintf(L%s service...\n, lpDependencies->lpServiceName);
ess = *(lpDependencies + i);
// Open the service
hDepService = OpenService(hSCM, ess.lpServiceName, SERVICE_STOP | SERVICE_QUERY_STATUS);
if ( !hDepService )
return GetLastError();
__try {
// Send a stop code
if ( !ControlService(hDepService, SERVICE_CONTROL_STOP, &ss) )
return GetLastError();
else
wprintf(LStopping %s ...\n, lpDependencies->lpServiceName);
// Wait for the service to stop
while (ss.dwCurrentState != SERVICE_STOPPED)
{
Sleep( ss.dwWaitHint );
if (!QueryServiceStatus(hDepService, &ss) )
return GetLastError();
if (ss.dwCurrentState == SERVICE_STOPPED)
{
wprintf(LDependencies %s service was stopped successfully!\n, lpDependencies->lpServiceName);
break;
}
if (GetTickCount() - dwStartTime > dwTimeout)
return ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
}
__finally
{
// Always release the service handle
CloseServiceHandle( hDepService);
}
}
}
__finally
{
// Always free the enumeration buffer
HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, lpDependencies);
}
}
}
// Send a stop code to the main service
if (!ControlService(hService, SERVICE_CONTROL_STOP, &ss) )
return GetLastError();
// Wait for the service to stop
while (ss.dwCurrentState != SERVICE_STOPPED)
{
Sleep( ss.dwWaitHint );
if (!QueryServiceStatus(hService, &ss) )
return GetLastError();
if (ss.dwCurrentState == SERVICE_STOPPED)
break;
if (GetTickCount() - dwStartTime > dwTimeout)
return ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
// Return success
return ERROR_SUCCESS;
}
//**********************************************************************
// DisplayError()
// PURPOSE : This is a helper function to display an error message if a function in wmain() fails.
// PARAMETERS: szAPI - the name of the function that failed
// dwError - the Win32 error code indicating why the function failed//
// RETURN VALUE: None
//**********************************************************************
void DisplayError( LPTSTR szAPI, DWORD dwError )
{
LPTSTR lpBuffer = NULL;
FormatMessage( FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER |
FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM, NULL, dwError,
MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), (LPTSTR) &lpBuffer, 0, NULL );
wprintf(L%s failed:\n, szAPI );
wprintf(L error code = %u\n, dwError );
wprintf(L message = %s\n, lpBuffer );
LocalFree( lpBuffer );
}
//**********************************************************************
// wmain() -- becomes main() for ANSI or wmain() for Unicode
// PURPOSE : This is the entry point for the program. This function
// contains sample code demonstrating how to use the
// StopService() function implemented above.
// PARAMETERS: argc - the number of command-line arguments
// argv[] - an array of command-line arguments
// RETURN VALUE: None
//**********************************************************************
void wmain(int argc, WCHAR *argv[] )
{
SC_HANDLE hSCM;
SC_HANDLE hService;
DWORD dwError;
if ( argc < 2 )
{
wprintf(LUsage: \%s\ <ServiceName>\n, argv[0] );
return;
}
__try
{
// Open the SCM database
hSCM = OpenSCManager( NULL, NULL, SC_MANAGER_CONNECT );
if ( !hSCM )
{
DisplayError(LOpenSCManager(), GetLastError() );
__leave;
}
// Open the specified service
hService = OpenService( hSCM, argv[1], SERVICE_STOP | SERVICE_QUERY_STATUS | SERVICE_ENUMERATE_DEPENDENTS );
if ( !hService )
{
DisplayError(LOpenService(), GetLastError() );
__leave;
}
// Try to stop the service, specifying a 30 second timeout
dwError = StopService( hSCM, hService, TRUE, 30000 ) ;
if ( dwError == ERROR_SUCCESS )
wprintf(LThe main service, %s was stopped successfully!\n, argv[1] );
else
DisplayError(LStopService(), dwError );
}
__finally
{
if ( hService )
CloseServiceHandle( hService );
if ( hSCM )
CloseServiceHandle( hSCM );
}
}
Build the project and make sure there is no error.
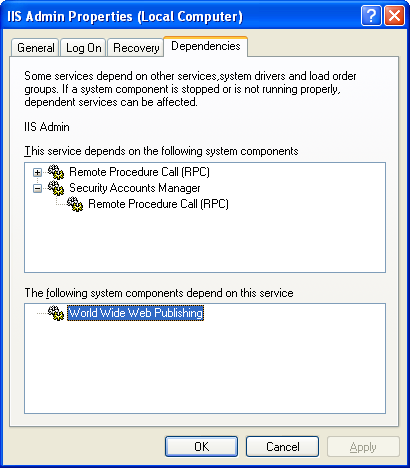
We will test the IIS Admin service which having the World Wide Web Publishing service dependency. This can be verified through the IIS Admin Properties page which can be invoked from Windows Services snap-in.
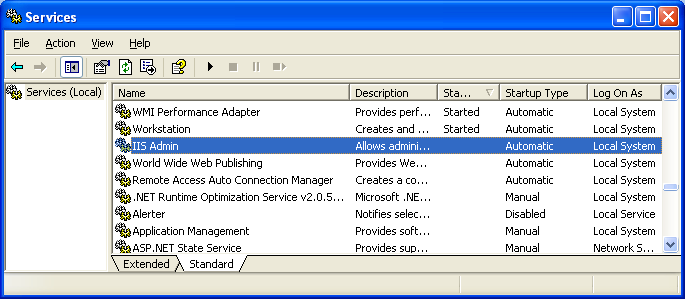
Try running the program with iisadmin (service name) service as the argument.

Then, do a verification using Windows Services snap-in.
Well, that all folks for this quite long session which covered a complete Windows services programming using Win32. More or 'missing information' can be found at Windows Service Reference.
< Windows Services 23 | Win32 Programming | Windows Services Win32 Programming | Windows Exception Handling >