Windows Services Programming 2
Introduction on Windows Services
The service control manager (SCM) maintains a database of installed services and driver services, and provides a unified and secure means of controlling them. The database includes information on how each service or driver service should be started. It also enables system administrators to customize security requirements for each service and thereby control access to the service. The following types of programs use the functions provided by the SCM.
|
Type |
Description |
|
Service program |
A program that provides executable code for one or more services. Service programs use functions that connect to the SCM and send status information to the SCM. |
|
Service configuration program |
A program that queries or modifies the services database. Service configuration programs use functions that open the database, install or delete services in the database, and query or modify the configuration and security parameters for installed services. Service configuration programs manage both services and driver services. |
|
Service control program |
A program that starts and controls services and driver services. Service control programs use functions that send requests to the SCM, which carries out the request. |
Service Control Manager
The service control manager (SCM) is started at system boot. It is a remote procedure call (RPC) server, so that service configuration and service control programs can manipulate services on remote machines. The service functions provide an interface for the following tasks performed by the SCM:
- Maintaining the database of installed services.
- Starting services and driver services either upon system startup or upon demand.
- Enumerating installed services and driver services.
- Maintaining status information for running services and driver services.
- Transmitting control requests to running services.
- Locking and unlocking the service database.
The following sections describe the SCM in more detail.
Database of Installed Services
The SCM maintains a database of installed services in the registry. The database is used by the SCM and programs that add, modify, or configure services. The following is the registry key for this database:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services
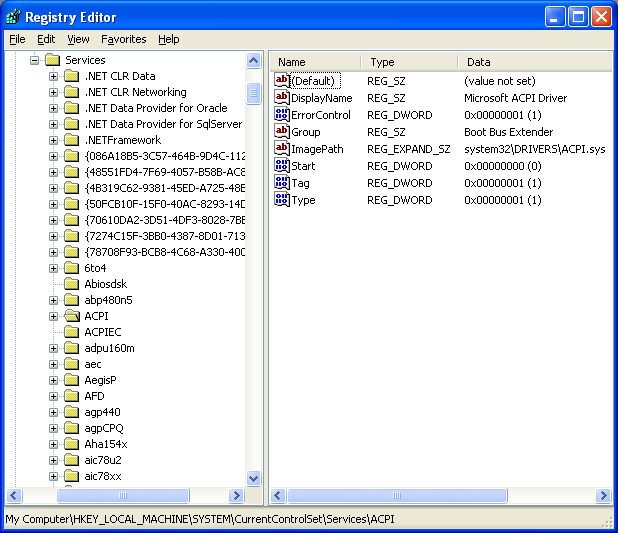
This key contains a subkey for each installed service and driver service. The name of the subkey is the name of the service, as specified by the CreateService() function when the service was installed by a service configuration program. An initial copy of the database is created when the system is installed. The database contains entries for the device drivers required during system boot. The database includes the following information about each installed service and driver service:
- The service type. This indicates whether the service executes in its own process or shares a process with other services. For driver services, this indicates whether the service is a kernel driver or a file system driver.
- The start type. This indicates whether the service or driver service is started automatically at system startup (auto-start service) or whether the SCM starts it when requested by a service control program (demand-start service). The start type can also indicate that the service or driver service is disabled, in which case it cannot be started.
- The error control level. This specifies the severity of the error if the service or driver service fails to start during system startup and determines the action that the startup program will take.
- The fully qualified path of the executable file. The filename extension is .EXE for services and .SYS for driver services.
- Optional dependency information used to determine the proper order for starting services or driver services. For services, this information can include a list of services that the SCM must start before it can start the specified service, the name of a load ordering group that the service is part of, and a tag identifier that indicates the start order of the service in its load ordering group. For driver services, this information includes a list of drivers that must be started before the specified driver.
- For services, an optional account name and password. The service program runs in the context of this account. If no account is specified, the service executes in the context of the LocalSystem account.
- For driver services, an optional driver object name (for example, \FileSystem\Rdr or \Driver\Xns), used by the I/O system to load the device driver. If no name is specified, the I/O system creates a default name based on the driver service name.
This database is also known as the ServicesActive database or the SCM database. You must use the functions provided by the SCM, instead of modifying the database directly.
< Windows Services 1 | Win32 Programming | Windows Services Win32 Programming | Windows Services 3 >