Windows Thread Synchronization 31
Using One-Time Initialization Program Example
The following examples demonstrate the use of the one-time initialization functions.
The Synchronous Example
The g_InitOnce global variable is the one-time initialization structure. The OpenEventHandleSync() function returns a handle to an event that is created only once, or INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE. It calls the InitOnceExecuteOnce() function to execute the initialization code contained in the InitHandleFunction() callback function. InitHandleFunction() calls the CreateEvent() function to create the event and returns the event handle in the lpContext parameter. If the callback function succeeds, OpenEventHandleAsync() returns the event handle returned in lpContext; otherwise, it returns INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE.
Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.
Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.
Next, add the following source code.
// Min Vista/Server 2008
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0600
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// Global variable
INIT_ONCE g_InitOnce;
BOOL CALLBACK InitHandleFunction (
PINIT_ONCE InitOnce,
PVOID Parameter,
PVOID *lpContext)
{
HANDLE hEvent;
hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, TRUE, TRUE, NULL);
if (NULL == hEvent)
{
wprintf(LCreateEvent() failed, error %d\n, GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
else
{
wprintf(LCreateEvent() is OK\n);
*lpContext = hEvent;
return TRUE;
}
}
HANDLE OpenEventHandleSync()
{
PVOID lpContext;
BOOL bStatus;
bStatus = InitOnceExecuteOnce(&g_InitOnce, InitHandleFunction, NULL, &lpContext);
if (bStatus)
{
wprintf(LInitOnceExecuteOnce() is OK...\n);
return (HANDLE)lpContext;
}
else
{
wprintf(LInitOnceExecuteOnce() failed, error %d\n, GetLastError());
return (INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE);
}
}
int wmain()
{
OpenEventHandleSync();
return 0;
}
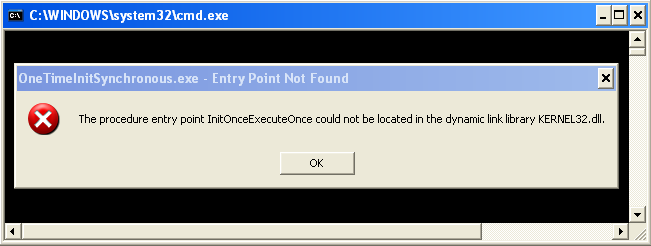
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output when running on Win XP Pro.
< Thread Synchronization 30 | Thread Synchronization Programming | Win32 Programming | Thread Synchronization 32 >