Windows Process Status Helpers API 2
Using PSAPI: Program Examples
The following examples demonstrate how to use the PSAPI functions:
- Enumerating all processes
- Enumerating all modules for a process
- Enumerating all device drivers in the system
- Collecting memory usage information for a process
- Taking a Snapshot and Viewing Processes
Enumerating All Processes Program Example
The following sample code uses the EnumProcesses() function to enumerate the current processes in the system.
Create new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.

Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.

Next, add the following source code.
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// Kernel32.lib on Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2,
// Psapi.lib on Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista,
// Windows Server 2003, and Windows XP/2000
#include <psapi.h>
// Another way to link to the desired library, we can use
// the following pragma directive
// #pragma comment(lib, Psapi.lib)
void PrintProcessNameAndID(DWORD processID)
{
WCHAR szProcessName[MAX_PATH] = L<Unknown>;
static int i;
HMODULE hMod;
DWORD cbNeeded;
// Get a handle to the process.
HANDLE hProcess = OpenProcess( PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, processID );
// Get the process name.
if (hProcess != NULL)
{
if (EnumProcessModules(hProcess, &hMod, sizeof(hMod), &cbNeeded))
{
GetModuleBaseName(hProcess, hMod, szProcessName, sizeof(szProcessName)/sizeof(WCHAR));
}
}
// Print the process name and identifier.
wprintf(LProcess #%i: %s\t(PID: %u)\n, i, szProcessName, processID);
i++;
CloseHandle(hProcess);
/*
if(CloseHandle(hProcess) != 0)
wprintf(LhProcess handle was closed successfully!\n);
else
wprintf(LFailed to close hProcess handle! Error %d\n, GetLastError());
*/
}
int wmain(int argc, WCHAR **argv)
{
// Get the list of process identifiers.
DWORD aProcesses[1024], cbNeeded, cProcesses;
unsigned int i;
if (!EnumProcesses(aProcesses, sizeof(aProcesses), &cbNeeded))
return 1;
else
wprintf(LEnumProcesses() is OK!\n);
// Calculate how many process identifiers were returned.
cProcesses = cbNeeded / sizeof(DWORD);
// Print the name and process identifier for each process.
for (i = 0; i < cProcesses; i++)
if(aProcesses[i] != 0)
PrintProcessNameAndID(aProcesses[i]);
return 0;
}
Add the Additional Dependencies.
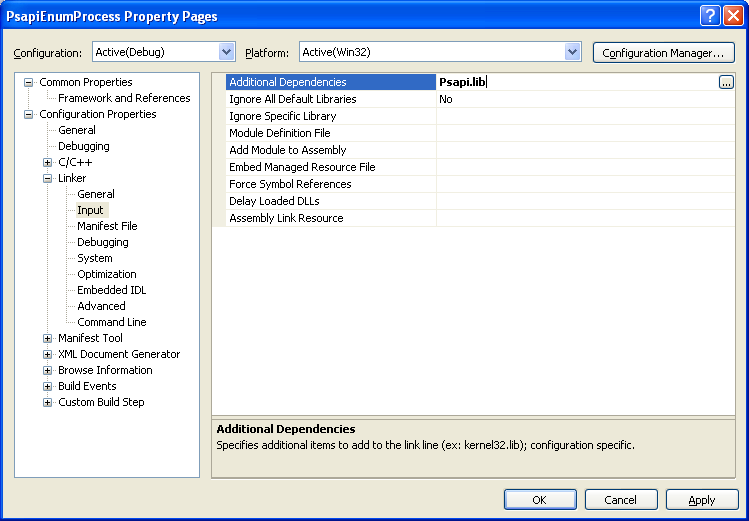
Another way to link to the library, we can use the #pragma directive and the following is for this example.
#pragma comment(lib, Psapi.lib)
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.

The main function obtains a list of processes by using the EnumProcesses() function. For each process, main calls the PrintProcessNameAndID() function, passing it the process identifier. PrintProcessNameAndID() in turn calls the OpenProcess() function to obtain the process handle. If OpenProcess() fails, the output shows the process name as <unknown>. For example, OpenProcess() fails for the Idle and CSRSS processes because their access restrictions prevent user-level code from opening them. Next, PrintProcessNameAndID() calls the EnumProcessModules() function to obtain the module handles. Finally, PrintProcessNameAndID() calls the GetModuleBaseName() function to obtain the name of the executable file and displays the name along with the process identifier.
< Win32 Process Status Help APIs 1 | Process Status Help APIs Index | Win32 Programming | Win32 Process Status Help APIs 3 >