The Win32 Network Management APIs 19
Looking Up Text for Error Code Numbers Program Example
It is sometimes necessary to display error text associated with error codes returned from networking-related functions. You may need to perform this task with the network management functions provided by the system. The error text for these messages is found in the message table file named Netmsg.dll, which is found in %systemroot%\system32. This file contains error messages in the range NERR_BASE (2100) through MAX_NERR(NERR_BASE+899). These error codes are defined in the SDK header file lmerr.h.
The LoadLibrary() and LoadLibraryEx() functions can load Netmsg.dll. The FormatMessage() function maps an error code to message text, given a module handle to the Netmsg.dll file. The following sample illustrates how to display error text associated with network management functions, in addition to displaying error text associated with system-related error codes. If the supplied error number is in a specific range, the netmsg.dll message module is loaded and used to look up the specified error number with the FormatMessage() function.
Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give the project name and change the project location is needed.
Then, add the source file. Give it a name.
Then, add the following source code.
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <lmerr.h>
#define RTN_OK 0
#define RTN_USAGE 1
#define RTN_ERROR 13
void DisplayErrorText(DWORD dwLastError);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
fwprintf(stderr,LUsage: %s <error number>\n, argv[0]);
return RTN_USAGE;
}
DisplayErrorText(atoi(argv[1]));
return RTN_OK;
}
void DisplayErrorText(DWORD dwLastError)
{
HMODULE hModule = NULL; // default to system source
LPSTR MessageBuffer;
DWORD dwBufferLength;
DWORD dwFormatFlags = FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM ;
// https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa370674%28VS.85%29.aspx
// If dwLastError is in the network range, load the message source.
// NERR_BASE = 1200
if(dwLastError >= NERR_BASE && dwLastError <= MAX_NERR)
{
hModule = LoadLibraryEx(
TEXT(netmsg.dll),
NULL,
LOAD_LIBRARY_AS_DATAFILE
);
if(hModule != NULL)
dwFormatFlags |= FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_HMODULE;
}
// Call FormatMessage() to allow for message
// text to be acquired from the system or from the supplied module handle.
if(dwBufferLength = FormatMessageA(
dwFormatFlags,
hModule, // module to get message from (NULL == system)
dwLastError,
MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), // default language
(LPSTR) &MessageBuffer,
0,
NULL
))
{
DWORD dwBytesWritten;
// Output message string on stderr.
WriteFile(
GetStdHandle(STD_ERROR_HANDLE),
MessageBuffer,
dwBufferLength,
&dwBytesWritten,
NULL);
// Free the buffer allocated by the system.
LocalFree(MessageBuffer);
}
// If we loaded a message source, unload it.
if(hModule != NULL)
FreeLibrary(hModule);
}
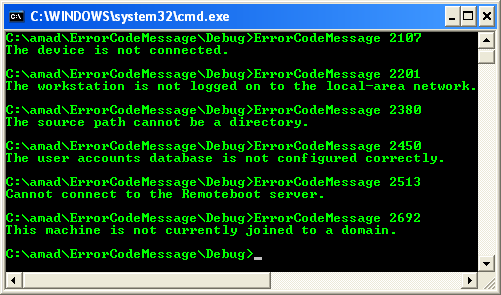
After you compile this program, you can insert the error code number as an argument and the program will display the text.
The following code shows the Unicode version.
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <lmerr.h>
#define RTN_OK 0
#define RTN_USAGE 1
#define RTN_ERROR 13
VOID DisplayErrorText(DWORD dwLastError);
int wmain(int argc, WCHAR *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
fwprintf_s(stderr,LUsage: %s <error number>\n, argv[0]);
fwprintf_s(stderr,LExample: %s 1234\n, argv[0]);
return RTN_USAGE;
}
DisplayErrorText(_wtoi(argv[1]));
return RTN_OK;
}
void DisplayErrorText(DWORD dwLastError)
{
HMODULE hModule = NULL; // default to system source
LPSTR MessageBuffer;
DWORD dwBufferLength;
DWORD dwFormatFlags = FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER |FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS |FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM;
// https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa370674%28VS.85%29.aspx
// If dwLastError is in the network range, load the message source.
if(dwLastError >= NERR_BASE && dwLastError <= MAX_NERR)
{
hModule = LoadLibraryEx(Lnetmsg.dll,NULL,LOAD_LIBRARY_AS_DATAFILE);
if(hModule != NULL)
dwFormatFlags |= FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_HMODULE;
}
// Call FormatMessage() to allow for message
// text to be acquired from the system or from the supplied module handle.
if(dwBufferLength = FormatMessageA(
dwFormatFlags,
hModule, // module to get message from (NULL == system)
dwLastError,
MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), // default language
(LPSTR) &MessageBuffer,
0,
NULL))
{
DWORD dwBytesWritten;
// Output message string on stderr.
WriteFile(GetStdHandle(STD_ERROR_HANDLE),MessageBuffer,dwBufferLength,&dwBytesWritten,NULL);
// Free the buffer allocated by the system.
LocalFree(MessageBuffer);
}
// If we loaded a message source, unload it.
if(hModule != NULL)
FreeLibrary(hModule);
}
< Win32 Network Management APIs 18 | Win32 Network Management APIs | Win32 Programming | Win32 Network Management APIs 20 >