Windows Access Control List (ACL) Example 20
Modifying the SACL and Privilege Program Example
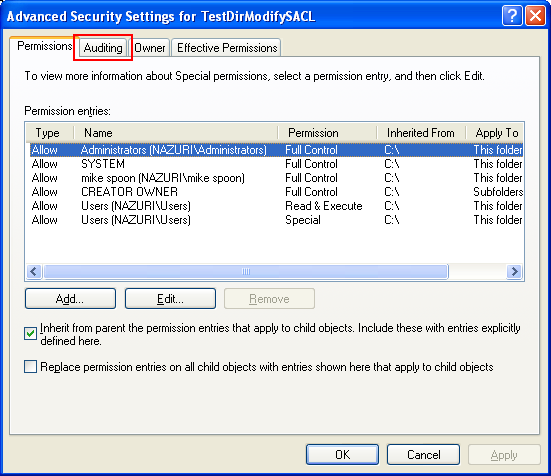
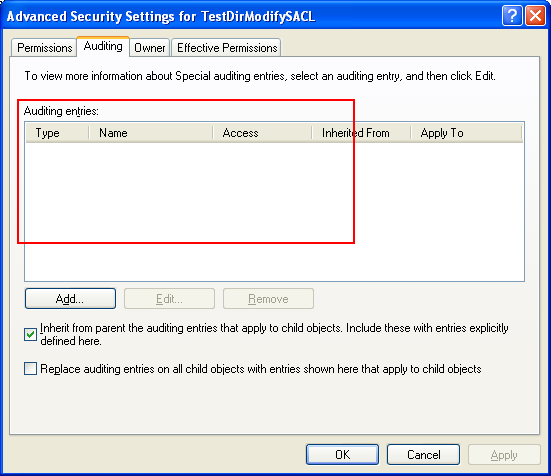
The following program example tries to modify the SACL. Before we run the program example, we create a directory named C:\TestDirModifySACL. The directory property pages before the program is run, shows there is no ACE in the Auditing entries. We will add an entry (SACL) to the ACE for auditing which needs a privilege.

Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.
Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.

Next, add the following source code.
// Modifying ACL (SACL) of an object.
// Here we are going to add Allow standard right access and SACL.
// This Win XP machine is logged in by user named Mike spoon who
// is a member of Administrators group...
// To access a SACL using the GetNamedSecurityInfo() or
// SetNamedSecurityInfo() functions, we have to enable the SE_SECURITY_NAME privilege
#include <windows.h>
#include <aclapi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// ********** Enabling/disabling the privilege ***************
BOOL SetPrivilege(
HANDLE hToken, // access token handle
LPCTSTR lpszPrivilege, // name of privilege to enable/disable
BOOL bEnablePrivilege // to enable (or disable privilege)
)
{
TOKEN_PRIVILEGES tp;
LUID luid;
if(!LookupPrivilegeValue(
NULL, // lookup privilege on local system
lpszPrivilege, // privilege to lookup
&luid)) // receives LUID of privilege
{
wprintf(LLookupPrivilegeValue() failed, error: %u\n, GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
else
wprintf(LLookupPrivilegeValue() is OK, %s found!\n, lpszPrivilege);
// the number of entries in the Privileges array
tp.PrivilegeCount = 1;
// an array of LUID_AND_ATTRIBUTES structures
tp.Privileges[0].Luid = luid;
// If TRUE
if(bEnablePrivilege)
{
tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED;
wprintf(LPrivilege was enabled!\n);
}
else
{
tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = 0;
wprintf(LPrivilege was disabled!\n);
}
// Enable the privilege (or disable all privileges)
if(!AdjustTokenPrivileges(
hToken,
FALSE, // If TRUE, function disables all privileges,
// if FALSE the function modifies privileges based on the tp
&tp,
sizeof(TOKEN_PRIVILEGES),
(PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES) NULL,
(PDWORD) NULL))
{
wprintf(LAdjustTokenPrivileges() failed, error: %u\n, GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
else
wprintf(LAdjustTokenPrivileges() is OK!\n);
return TRUE;
}
// Clean up routine
void Cleanup(PSECURITY_DESCRIPTOR pSS, PACL pNewSACL)
{
if(pSS != NULL)
LocalFree((HLOCAL) pSS);
else
wprintf(LpSS freed...\n);
if(pNewSACL != NULL)
LocalFree((HLOCAL) pNewSACL);
else
wprintf(LpNewSACL freed...\n);
}
int wmain(int argc, WCHAR **argv)
{
// Handle to the running process that is this program
HANDLE hToken;
BOOL bTestRetVal = FALSE;
// Initially we try to enable
BOOL bEnablePrivilege = TRUE;
// The needed privilege
LPCTSTR lpszPrivilege = LSeSecurityPrivilege;
// Name of object, here we will add an ACE for a directory
LPTSTR pszObjName = LC:\\TestDirModifySACL;
// type of object, file or directory, a directory
SE_OBJECT_TYPE ObjectType = SE_FILE_OBJECT;
// Access mask for new ACE equal to 0X11000000 - GENERIC_ALL and ACCESS_SYSTEM_SECURITY
DWORD dwAccessRights = 0X11000000;
// type of ACE, set audit for success
ACCESS_MODE AccessMode = SET_AUDIT_SUCCESS;
// Inheritance flags for new ACE. The OBJECT_INHERIT_ACE and CONTAINER_INHERIT_ACE flags are
// not propagated to an inherited ACE.
DWORD dwInheritance = NO_PROPAGATE_INHERIT_ACE;
// format of trustee structure, the trustee is name
TRUSTEE_FORM TrusteeForm = TRUSTEE_IS_NAME;
// The new trustee for the ACE is set to Johnny (logon name, full name is John Doe),
// a valid normal user f the local computer. However, this program run by user Mike spoon
// Change accordingly...
LPTSTR pszTrustee = LJohnny;
// Result
DWORD dwRes = 0;
// Existing and new SACL pointers...
PACL pOldSACL = NULL, pNewSACL = NULL;
// Security descriptor
PSECURITY_DESCRIPTOR pSS = NULL;
// EXPLICIT_ACCESS structure
EXPLICIT_ACCESS ea;
// Verify the object name validity
if(pszObjName == NULL)
{
wprintf(LThe object name is not valid!\n);
return ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
else
wprintf(LThe object name is valid!\n);
//**************Privilege routine here*****************
//*************** Get the handle to the process ****************
// Open a handle to the access token for the calling process.
if(!OpenProcessToken(GetCurrentProcess(), TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES, &hToken))
{
wprintf(LOpenProcessToken() failed, error %u\n, GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
else
wprintf(LOpenProcessToken() is OK, got the handle!\n);
//************ Enabling privilege ******************
// Call the user defined SetPrivilege() function to enable privilege
wprintf(LEnabling the privilege...\n);
bTestRetVal = SetPrivilege(hToken, lpszPrivilege, bEnablePrivilege);
// Verify
wprintf(LThe SetPrivilage() return value: %d\n\n, bTestRetVal);
//*************** End enabling privilege *********************
// Get a pointer to the existing SACL.
dwRes = GetNamedSecurityInfo(pszObjName,
ObjectType,
SACL_SECURITY_INFORMATION,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
&pOldSACL,
&pSS);
// Verify
if(dwRes != ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
wprintf(LGetNamedSecurityInfo() failed, error %u\n, dwRes);
Cleanup(pSS, pNewSACL);
}
else
wprintf(LGetNamedSecurityInfo() is working!\n);
// Initialize an EXPLICIT_ACCESS structure for the new ACE.
// If more entries needed, you can create an array
// of the ea variable of the EXPLICIT_ACCESS
ZeroMemory(&ea, sizeof(EXPLICIT_ACCESS));
ea.grfAccessPermissions = dwAccessRights;
ea.grfAccessMode = AccessMode;
ea.grfInheritance= dwInheritance;
ea.Trustee.TrusteeForm = TrusteeForm;
// Other structure elements...
// ea.Trustee.TrusteeType = TRUSTEE_IS_GROUP;
// ea.Trustee.TrusteeType = TRUSTEE_IS_USER;
// The trustee is testuser
ea.Trustee.ptstrName = pszTrustee;
// Create a new ACL that merges the new ACE into the existing ACL.
dwRes = SetEntriesInAcl(1, &ea, pOldSACL, &pNewSACL);
if(dwRes != ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
wprintf(LSetEntriesInAcl() failed, error %u\n, dwRes);
Cleanup(pSS, pNewSACL);
}
else
wprintf(LSetEntriesInAcl() is pretty fine!\n);
// Attach the new ACL as the object's SACL.
dwRes = SetNamedSecurityInfo(pszObjName,
ObjectType,
SACL_SECURITY_INFORMATION,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
pNewSACL);
if(dwRes != ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
wprintf(LSetNamedSecurityInfo() failed, error %u\n, dwRes);
Cleanup(pSS, pNewSACL);
}
else
wprintf(LSetNamedSecurityInfo() is OK!\n);
//************* Disable the privilege ****************
wprintf(LDisabling the privilege...\n);
bEnablePrivilege = FALSE;
SetPrivilege(hToken, lpszPrivilege, bEnablePrivilege);
// Verify
wprintf(LThe SetPrivilage() return value: %d\n\n, bTestRetVal);
//************* End disabling the privilege ****************
return 0;
}
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.

From the program output and the Advanced Security Setting for C:\TestDirModifySACL directory property pages as shown below, we can see that an entry was added for auditing.


< Windows ACL Example 19 | Windows Access Control List (ACL) Main | Win32 Programming | Windows ACL Example 21 >