The Windows File Management 6
File Type, Size and Timestamp Program Example
The following program example demonstrates the use of file type, file size and timestamp functions.
Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.
Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.
Next, add the following source code.
// FileWriteLastTime - Retrieves the last-write time and converts the time to a string
// Return value - TRUE if successful, FALSE otherwise
// hFile - Valid file handle
// lpszString - Pointer to buffer to receive string
#include <windows.h>
#include <strsafe.h>
// A prototype that receives a function name, displaying
// system error code and its respective message
void DisplayErrorBox(LPTSTR lpszFunction);
BOOL GetLastWriteTime(HANDLE hFile, LPTSTR lpszString, DWORD dwSize)
{
FILETIME ftCreate, ftAccess, ftWrite;
SYSTEMTIME stUTC, stLocal;
DWORD dwRet;
// Retrieve the file times for the file.
if (!GetFileTime(hFile, &ftCreate, &ftAccess, &ftWrite))
return FALSE;
// Convert the last-write time to local time.
FileTimeToSystemTime(&ftWrite, &stUTC);
SystemTimeToTzSpecificLocalTime(NULL, &stUTC, &stLocal);
// Build a string showing the date and time.
dwRet = StringCchPrintf(lpszString, dwSize,
L%02d/%02d/%d %02d:%02d,
stLocal.wMonth, stLocal.wDay, stLocal.wYear,
stLocal.wHour, stLocal.wMinute);
if(S_OK == dwRet)
return TRUE;
else return FALSE;
}
int wmain(int argc, WCHAR *argv[])
{
HANDLE hFile;
WCHAR szBuf[MAX_PATH];
DWORD dwFileType = 0;
LARGE_INTEGER lpFileSize;
BOOL bRetVal;
if(argc != 2)
{
wprintf(LThis sample takes a file name as an argument\n);
wprintf(L%s <file_name_to_check>\n, argv[0]);
wprintf(L%s C:\\anothertestfile.doc\n, argv[0]);
// Non-zero means error
return 1;
}
hFile = CreateFile(argv[1], GENERIC_READ, FILE_SHARE_READ, NULL, OPEN_EXISTING, 0, NULL);
if(hFile == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
DisplayErrorBox(LCreateFile());
return 1;
}
else
wprintf(LCreateFile() is pretty fine!\n);
dwFileType = GetFileType(hFile);
switch(dwFileType)
{
case FILE_TYPE_CHAR: wprintf(L%s is a character file, typically an LPT device or a console.\n, argv[1]);
break;
case FILE_TYPE_DISK: wprintf(L%s is a disk file\n, argv[1]);
break;
case FILE_TYPE_PIPE: wprintf(L%s is a socket, a named pipe, or an anonymous pipe.\n, argv[1]);
break;
case FILE_TYPE_UNKNOWN: wprintf(L%s is unknown, or the function failed!\n, argv[1]);
break;
default:
wprintf(L%s is unknown type!\n, argv[1]);
}
bRetVal = GetFileSizeEx(hFile, &lpFileSize);
// TRUE
if(bRetVal != 0)
{
wprintf(LGetFileSizeEx() looks fine!\n);
wprintf(LFile size is %u bytes\n, lpFileSize.QuadPart);
}
else
DisplayErrorBox(LGetFileSizeEx());
if(GetLastWriteTime(hFile, szBuf, MAX_PATH))
wprintf(LLast write time is: %s\n, szBuf);
if(CloseHandle(hFile) != 0)
wprintf(LhFile handle was closed successfully!\n);
else
DisplayErrorBox(LCloseHandle());
return 0;
}
void DisplayErrorBox(LPTSTR lpszFunction)
{
// Retrieve the system error message for the last-error code
LPVOID lpMsgBuf;
LPVOID lpDisplayBuf;
DWORD dw = GetLastError();
FormatMessage(
FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER |
FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM |
FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS,
NULL,
dw,
MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT),
(LPTSTR) &lpMsgBuf,
0, NULL );
// Display the error message and clean up
lpDisplayBuf = (LPVOID)LocalAlloc(LMEM_ZEROINIT, (lstrlen((LPCTSTR)lpMsgBuf)+lstrlen((LPCTSTR)lpszFunction)+40)*sizeof(WCHAR));
StringCchPrintf((LPTSTR)lpDisplayBuf, LocalSize(lpDisplayBuf) / sizeof(WCHAR), L%s failed with error %d: %s, lpszFunction, dw, lpMsgBuf);
MessageBox(NULL, (LPCTSTR)lpDisplayBuf, LError, MB_OK);
LocalFree(lpMsgBuf);
LocalFree(lpDisplayBuf);
}
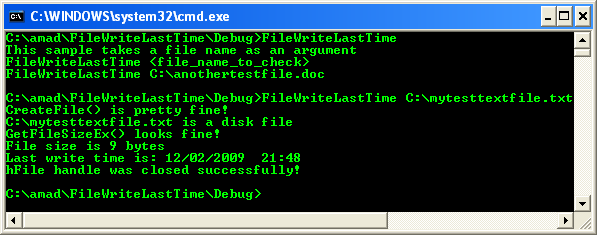
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.
< Windows Files 5 | Win32 Programming | Win32 File Index | Windows Files 7 >