Windows Thread Synchronization 48
Managing Multiple Threads Program Example
In the next two examples, numerous threads are created that terminate at random times. Their termination and display messages are then caught to indicate their termination status.
Multiple Threads Example
Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.
Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.
Next, add the following source code.
#include <Windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 5
DWORD WINAPI thread_function(LPVOID arg)
{
int t_number = *(int *)arg;
int rand_delay;
wprintf(Lthread_function() is running. Arg received was %u, thread ID is %u\n, t_number, GetCurrentThreadId());
// Seed the random-number generator with
// current time so that the numbers will
// be different each time function is run.
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
// random time delay from 1 to 10
rand_delay = 1 + (rand() % 10);
Sleep(rand_delay*1000);
wprintf(LBye from thread #%d, ID %u\n, t_number, GetCurrentThreadId());
wprintf(L\n);
return 100;
}
int wmain()
{
HANDLE a_thread[NUM_THREADS];
int multiple_threads, j;
for(multiple_threads = 0; multiple_threads < NUM_THREADS; multiple_threads++)
{
// Create a new thread.
a_thread[multiple_threads] = CreateThread(NULL, 0, thread_function,(LPVOID)&multiple_threads, 0,NULL);
if (a_thread[multiple_threads] == NULL)
{
wprintf(LCreateThread() - Thread creation failed, error %u\n, GetLastError());
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
Sleep(1000);
}
wprintf(LWaiting for threads to finish...\n);
for(multiple_threads = NUM_THREADS - 1; multiple_threads >= 0; multiple_threads--)
{
if (WaitForSingleObject(a_thread[multiple_threads],INFINITE) == WAIT_OBJECT_0)
{
wprintf(LWaitForSingleObject() - Another thread signaled...\n);
}
else
{
wprintf(LWaitForSingleObject() failed, error %u\n, GetLastError());
}
}
wprintf(L\n);
for(j=0;j<NUM_THREADS;j++)
{
if(CloseHandle(a_thread[j]) != 0)
wprintf(La_thread[%u] handle was successfully closed!\n, j);
else
wprintf(LFailed to close a_thread[%u] handle, error %u\n, j, GetLastError());
}
wprintf(LAll done!\n);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
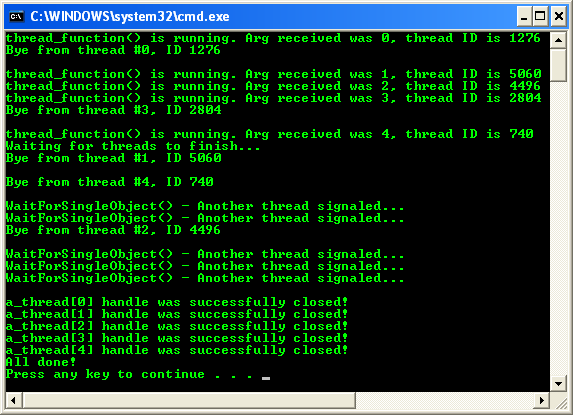
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.
More: Synchronization Reference
The following constructs are used with synchronization in Windows. You should explore them when needed.
< Thread Synchronization 47 | Thread Synchronization Programming | Win32 Programming | Windows Process Tool Help APIs >