Windows Thread Synchronization 23
Another Semaphore Program Example
Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.

Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.
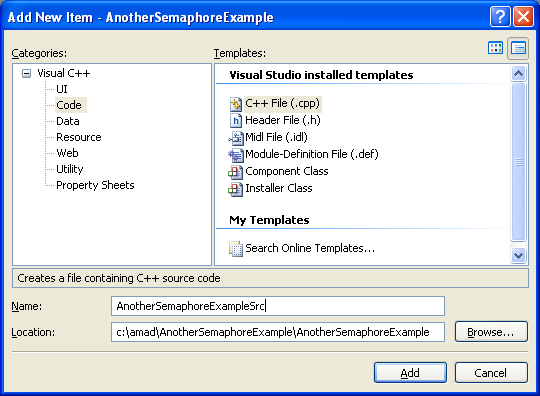
Next, add the following source code.
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
// handle to semaphore
HANDLE hSem=NULL;
///////////////// Thread Code //////////////////////////
void ChildThread(char *name)
{
BOOL bContinue=TRUE;
DWORD dwWaitResult;
while(bContinue)
{
// Waits until the specified object is in the signaled state or
// the time-out interval elapses.
// INFINITE - the function will return only when the object is signaled.
// Try to enter the semaphore gate.
dwWaitResult = WaitForSingleObject(
hSem, // handle to semaphore
INFINITE);
switch (dwWaitResult)
{
// The semaphore object was signaled.
case WAIT_OBJECT_0:
// TODO: Perform task
wprintf(LThread %d, %S: wait succeeded\n, GetCurrentThreadId(), name);
bContinue=FALSE;
// Simulate thread spending time on task
wprintf(L%S is working!\n, name);
Sleep(100);
break;
// The semaphore was nonsignaled, so a time-out occurred.
case WAIT_TIMEOUT:
wprintf(LThread %d: wait timed out\n, GetCurrentThreadId());
break;
}
}
}
/////// Create Threads ////////////
// returns TotalCount of Children created
int CreateChildren(void)
{
int i;
char *ThreadNames[7]={ThreadA,ThreadB,ThreadC,ThreadD,ThreadE,ThreadF, ThreadG};
for(i=0;i<7;++i)
{
HANDLE hThred;
DWORD dwThreadID;
hThred=CreateThread(NULL,0,(LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)ChildThread,(LPVOID)ThreadNames[i],0,&dwThreadID);
if(hThred!=NULL)
{
wprintf(LCreateThread() is OK, ID is %d, %S\n, dwThreadID, ThreadNames[i]);
if(CloseHandle(hThred) != 0)
wprintf(L hThred handle was closed successfully!\n);
else
wprintf(LFailed to close hThred handle, error %d\n, GetLastError());
}
else
wprintf(LCreateThread() failed with error %d, GetLastError());
}
return i;
}
////// Main //////
int wmain(void)
{
int TotalChildren;
// Creates or opens a named or unnamed (anonymous) semaphore object.
hSem=CreateSemaphore(NULL,0,7,NULL);
if(hSem==NULL)
{
wprintf(LCreateSemaphore() failed, error %u\n, GetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
wprintf(LCreateSemaphore() is OK, got the handle to the Semaphore object...\n);
TotalChildren = CreateChildren();
wprintf(LTotal Child Threads: %d\n,TotalChildren);
// unblock all the threads
// Increases the count of the specified semaphore object by a specified amount.
if(ReleaseSemaphore(hSem,7,NULL) != 0)
wprintf(LReleaseSemaphore() is OK\n);
else
wprintf(LReleaseSemaphore() failed, error %d\n, GetLastError());
if(CloseHandle(hSem) != 0)
wprintf(LhSem handle was closed!\n);
else
wprintf(LFailed to close the hSem handle! Error %d\n, GetLastError());
ExitProcess(0);
return 0;
}
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.

< Thread Synchronization 22 | Thread Synchronization Programming | Win32 Programming | Thread Synchronization 24 >