Windows Thread Synchronization 17
Using Named Objects Program Examples
The following example illustrates the use of object names by creating and opening a named mutex.
The First Process Program Example
The first process uses the CreateMutex() function to create the mutex object. Note that this function succeeds even if there is an existing object with the same name.
Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.
Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.
Next, add the following source code.
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
// This process creates the mutex object
int wmain(void)
{
HANDLE hMutex;
wprintf(LA process (main()) is creating a mutex...\n);
hMutex = CreateMutex(
NULL, // default security descriptor
FALSE, // mutex not owned
LMyGedikMutex); // object name
if (hMutex == NULL)
wprintf(LCreateMutex() failed, error %d\n, GetLastError() );
else
if ( GetLastError() == ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS )
wprintf(LCreateMutex() opened an existing mutex...\n);
else
wprintf(LCreateMutex() has created a new mutex...\n);
// Keep this process around until the second process is run
wprintf(LWaiting the second process to open the existing mutex...\n);
_getwch();
if(CloseHandle(hMutex) != 0)
wprintf(LMutex's handle closed successfully!\n);
else
wprintf(LFailed to close the mutex's handle, error %d\n, GetLastError());
return 0;
}
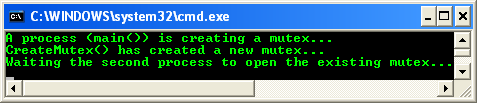
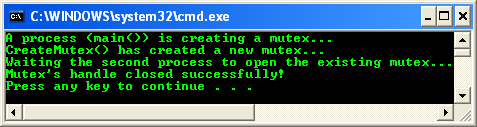
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.
< Thread Synchronization 16 | Thread Synchronization Programming | Win32 Programming | Thread Synchronization 18 >